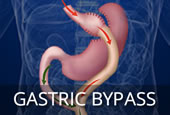
Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass Surgery
Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass Surgery is a very well established weight loss procedure. The stomach is first divided to create a small gastric pouch. Next, a Y-shaped section of intestine is fashioned and joined to the gastric pouch. This allows food to bypass the lower stomach and move directly into the intestines. The procedure may be performed laparoscopically (keyhole) but on occasions requires an open (large incision) approach.
The small gastric pouch limits the amount of food that is eaten by helping you feel full with a small meal, and the Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass Surgery amplifies this effect and reduces hunger by release of natural appetite inhibiting hormones in response to food entering the intestines earlier. As a result, weight loss is excellent and consistent.
Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass Surgery also has a specific effect on diabetes. Insulin function is enhanced by hormones released from the intestine triggered by food. In combination with weight loss, the effect on diabetes can be dramatic.
Eating with a Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass Surgery is often a little less demanding than with gastric banding, but again it is important to eat slowly and chew well.
Risks of Gastric Bypass Surgery
Being the most complex of the operations, the operative risk with Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass is also higher. The main issue is leak from the staple from any of the joins or staple lines, but bleeding, infection or general medical complications can also occur. The major complication rate is around 5-10%.
Advantages of Gastric Bypass Surgery
- Reliable, proven operation with consistent results
- No post-operative adjustments are required
- Particularly good results seen in Insulin dependent diabetics
- Average 65-80 % Excess Body Weight Loss
Disadvantages of Gastric Bypass Surgery
- Longer operating time and longer stay in hospital (4-7 nights)
- Leak from staple line where gastric pouch has been joined to small intestine (2-3%) which would prolong hospital stay and may require further intervention
- Greater nutritional surveillance required including more frequent blood tests, see below
Dietetic Requirements of Gastric Bypass
- A healthy, balanced eating plan is recommended with focus on portion control
- There is a greater risk of developing nutritional deficiencies due to the reduced volume of food that can be eaten and also due to the malabsorption that is surgically created. Most commonly deficiencies occur in Vitamin B12, Vitamin D, iron, folate, calcium and zinc. Hence these nutrients need to be closely monitored with regular blood tests
- Intolerance of high sugar foods can occur due to the changes in gut anatomy with this operation. ‘Dumping syndrome’ can result, causing dizziness, sweating, nausea and diarrhoea. To prevent this, high sugar foods and alcohol should be avoided
- At least 6-12 monthly review of nutritional adequacy (including annual blood tests) to ensure maintenance of adequate nutritional health.
Locations of Darebin Weight Loss Surgery
Key Consulting Locations
Suite 3, 195 Thompsons Road
Bulleen Vic 3105
Key Operating Locations
The Austin Hospital
Warringal Private Hospital
Epworth Richmond
Hospital
Latrobe Private
Northern Private.